The TIME function takes three numbers and converts them to time with hours, minutes, and seconds.
Furthermore, this function helps you use a time inside other formulas. Formulas do not understand times typed directly into a formula, as discussed in example 4.
In spreadsheets, time is a decimal value representing a fraction of a day ranging from 0 (midnight) to .9999884 (11:59 PM and 59 seconds).
If the result of the formula is not formatted correctly, first try the Time number formatting. Use the Custom date and time options in the menus for more adjustments.


Adjust the formatting until you get what you are looking for.
Contents
Syntax
=TIME(hour, minute, second)
hour – The number that represents the hour (0-23).
minute – A number that represents the minute (0-59).
second – The number that represents the second (0-59).
Related Functions
DATE – Similar to this function, the DATE function takes three numbers and converts them to a date.
MINUTE – Extracts the minute
HOUR – Extracts the hour
SECOND – Extracts the second
TIMEDIF – Google Sheets Add-On
Calculate any duration in:
- Years
- Months
- Weeks
- Days
- Hours
- Minutes
- Seconds
- Milliseconds
Errors
#VALUE! – The inputs aren’t valid numbers, such as “Half past three” or “In a sec”.
Examples
Example 1 – Outputs With Different Formatting
First, let’s look at a simple example of the time function. The spreadsheet shows the same output with three formatting types.

Here we see the function performing a simple conversion that results in 1:25:48 PM. However, the result is only shown as a time if the cell formatting is set to Time as it is in cell B5 in the example. In cell B6, we have applied the Date and time format. You should avoid this formatting since day 0 is December 30, 1899. See more about day 0 in this video. Lastly, formatting the output as a Number shows that times are fractions of 1. Since this result is a bit after midday, the decimal value is a bit more than .5.
Example 2 – Decimal Inputs for the Time Function
Second, we will look at what happens when one of the inputs is a decimal.

The function in cell D2 produces the same result as the previous example, even though the minutes are 25.1 instead of 25. This behavior is due to the decimal truncation instead of converting; in this case, 25.1 minutes to 25 minutes and 6 seconds.
Example 3 – Large Numbers as Inputs
For the third example, let’s look at what happens when we use inputs of more than 23 hours, 59 minutes, or 59 seconds.
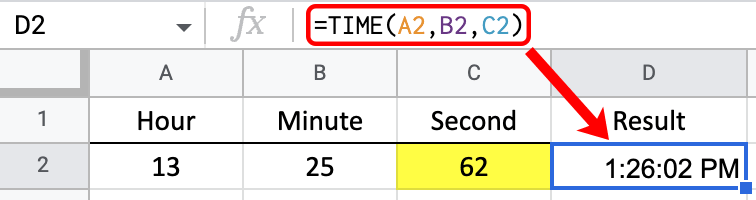
The second argument accepts numbers from 0 to 59. However, you can give any three arguments larger numbers, and Google Sheets will use the entire number. For example, Google Sheets treats 62 seconds as 1 minute and 2 seconds.
Example 4 – Using the TIME Function in A Formula
Now that we understand how the function works let’s look at an example of its typical use.

Entering =15:19:47-13:25:48 directly into a cell produces an #N/A error. This error is because you need to use one of three special methods to use times in formulas. You can surround them in quotes, locate them in cell references, or produce them with a specialized function, as we have done in this example.
⚠️ Remember to change the formatting to Duration, so the time doesn’t have AM at the end.
Live Examples in Sheets
Go to this spreadsheet for examples of the above function that you can study and use anywhere.


